Products:
Filtrations
Strainers Contaminations separators Air separators Droplet eliminatorsCircuit Separators
Hydraulic Separators for boiler circuit Hydraulic Separators for refrigeration systems CollectorsPressure vessels
Pressure Vessels and Storage Tanks Expansion VesselsControlers
Stabilizing and top-up equipment Valves and ControlersTERMEN » Offer » Expansion Vessels » Expansion Vessel for drinking water
Expansion Vessel for drinking water
Expansion pressure vessels
TerNP – low-carbon steel
TerNP-S – high-alloy steel
Applications
Designed for protecting drinking water and domestic hot water systems and as a buffer tank in pressurizing systems.
Features
- suitable for drinking water (sanitary certificate)
- compensation of pressure increase due to temperature increase
- water hammer arresting
- water reserve at high demand
- prevents frequent water pump activation
- water circulation in the vessel
- replaceable diaphragm
Design
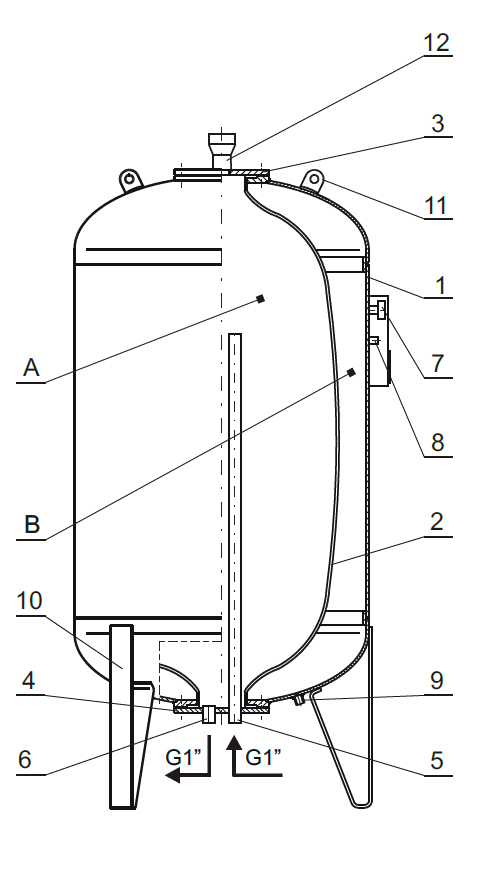
The expansion vessel is designed as a cylindrical steel tank (1) with a rubber diaphragm (2). A diaphragm is connected to the water system with two G1” ports (5, 6) to ensure water circulation in the tank. The expansion tank is vented with an automatic air vent (12) installed in the top cover (3). The tank shell is fitted with a pressure gauge (7) and pneumatic valve (8) for filling the gas chamber. The bottom heat is fitted with a port (9) for checking diaphragm integrity. Compact design allows to install large capacity vessels in rooms with standard door openings. The expansion vessels can be dismantled to replace the diaphragm (2).
Principle of operation
Chamber (A) is connected to the water system with two G1” ports (5, 6). Chamber (B) is filled with gas to initial pressure of 3 or 5 bar. As the medium pressure or volume increases or due to a water hammer, the diaphragm is filled with water to allow correct system operation. The system pressure increases to the value corresponding to the increase in gas pressure in chamber (B) corresponding to the reduction in gas chamber volume. By releasing or adding air with a pneumatic valve (8) the initial working pressure is adapted to the system requirements. The pressure in the gas chamber can be read on a pressure gauge (7). The vessel is fitted with two 1” connection ports for water circulation pump. The inlet port (5) supplies the medium to the top vessel section, whereas the outlet port (6) discharges the water from its bottom section. Chamber (A) is vented with an automatic air vent (12) installed on the top cover (3).